The type of ventilator used for different diseases is different. Generally speaking, single-level automatic ventilator is used for patients with snoring; the two-level ST mode ventilator for lung diseases. If it is a more complex snoring patient, it may be necessary to use Bilevel ventilator. The type of ventilator used for different diseases is different. There are multiple modes of non-invasive ventilator. The following describes the mode of the ventilator. You can choose the non-invasive ventilator suitable for you according to your own situation.
The ventilator has CPAP, S, T, S/T modes, as follows:
1. CPAP mode of ventilator: continuous positive airway pressure mode
CPAP: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Mode-Continuous Positive Airway Pressure, the patient has strong spontaneous breathing, the ventilator provides the same pressure in the inspiratory and expiratory phases to help the patient Open the airway. It is mainly used for patients with OSAS obstructive sleep apnea syndrome, strong spontaneous breathing, and only a little assistance from the ventilator. No trigger, no switching, the human body breathes freely, the pressure is controlled to a constant pressure, and the pressure of the inspiratory phase and the exhalation phase are equal. Assisted breathing (pressure support is 0) + pressure control is a more commonly used non-invasive mode. Physiological effects are equivalent to PEEP (positive end-expiratory pressure): increase functional residual volume, improve compliance; reduce inspiratory power consumption, improve triggering; maintain upper airway open state.
2. S mode of ventilator:
S mode of autonomous ventilation Spontaneous breathing mode --- Spontaneous breathing mode, the patient has spontaneous breathing or can trigger the ventilator to ventilate autonomously, the ventilator only provides IPAP and EPAP, the patient controls the breathing frequency and the inspiratory ratio/inspiratory time autonomously For patients with good spontaneous breathing or patients with central sleep apnea. Spontaneous breathing trigger: The ventilator and the patient's breathing frequency are fully synchronized. If the patient's spontaneous breathing stops, the ventilator also stops working. Pressure control (constant pressure): maintain a preset IPAP (inspiratory airway positive pressure) pressure on the inspiratory ventilator, and maintain a preset EPAP (expiratory airway positive pressure) pressure on the exhalation ventilator It is a flow rate switch, assisted breathing + pressure control, and is a relatively common non-invasive mode.
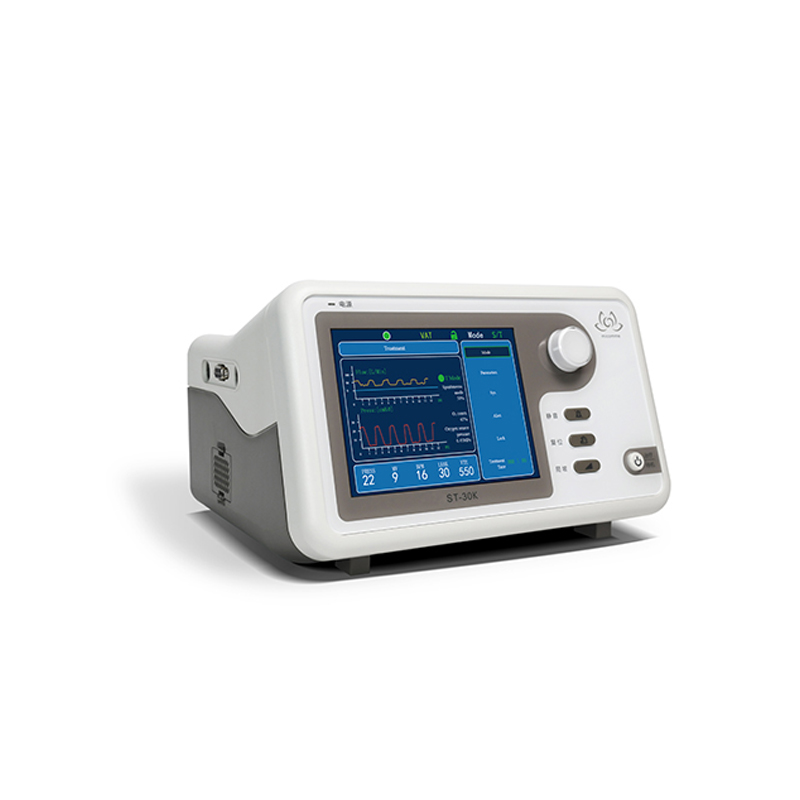
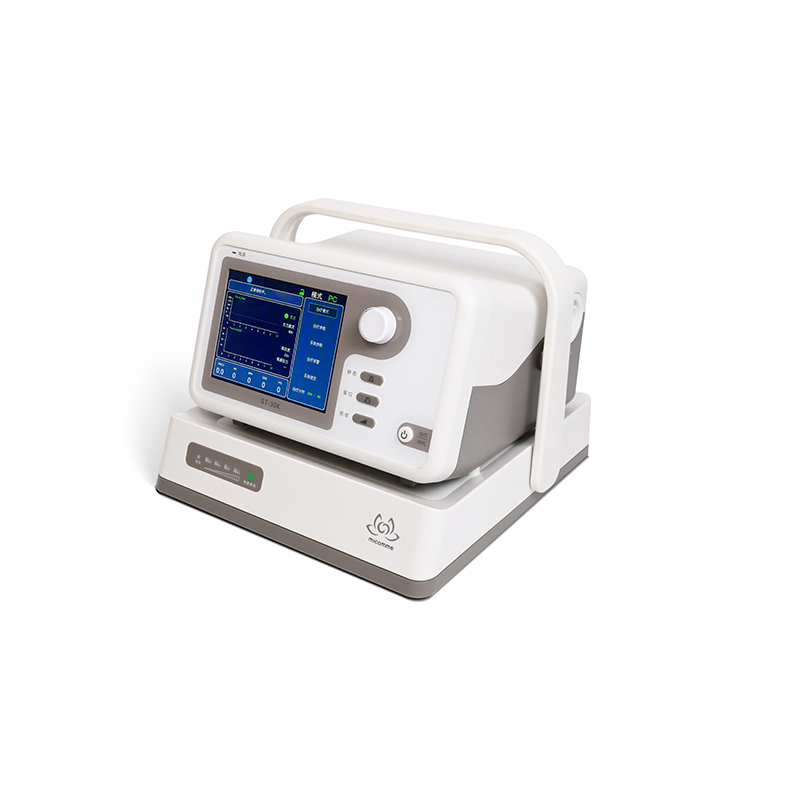
3. T mode of ventilator:
time ventilation mode T Time control mode-Timed time control mode, the patient has no spontaneous breathing or can not trigger the ventilator to ventilate independently, the ventilator fully controls the patient's breathing, provides IPAP (positive inspiratory phase airway pressure), EPAP (expiratory phase airway Positive pressure), BPM, Ti (inspiratory time/expiratory time ratio). This mode is mainly used for patients who have no spontaneous breathing or whose spontaneous breathing ability is weak. Time triggering: The ventilator works at a preset frequency and is not synchronized with the patient's spontaneous breathing. Pressure control (constant pressure): Maintain a preset IPAP (inspiratory airway positive pressure) pressure on the inspiratory ventilator, and maintain a preset EPAP (expiratory airway positive pressure) on the exhalation ventilator Pressure time switching: control breathing + pressure control, non-invasive mode rarely used.
4. S/T mode of ventilator:
autonomous/time ventilation mode S/T Spontaneous/Timed automatic switching mode --- Spontaneous/Timed automatic switching mode. When the patient's breathing cycle is less than the period corresponding to the backup ventilation frequency, it is in S mode; when the patient's breathing cycle is greater than the backup ventilation frequency, it is in T mode. Automatic switching point: the period corresponding to the backup ventilation frequency such as: BPM=10 times/min, breathing cycle=60 seconds/10=6 seconds, then the ventilator waits for 6 seconds, if the patient can trigger the ventilator within 6 seconds, the ventilator It is S working mode, otherwise it is T mode. This mode is the most commonly used and is used for various patients. a. The spontaneous breathing triggers when the spontaneous breathing frequency>preset frequency of the ventilator. The ventilator and the patient's breathing frequency are fully synchronized. The pressure control flow rate is switched. b. The spontaneous breathing frequency<time of the ventilator preset frequency. The ventilator triggers in advance. The set frequency working pressure control time switching assist/control breathing + pressure control is a commonly used non-invasive mode.
Post time: Jul-14-2020

